P
Rotation Representations: Quaternions
To overcome the singularity issue of Gimbal Lock found in Euler angles, we can use a different mathematical tool called quaternions.
What is a Quaternion?
At its core, a quaternion is a four-dimensional number. It's an extension of complex numbers, and it's written as:
where
For 3D rotations, it's more practical to think of a quaternion as having two parts: a scalar part (
To represent a rotation, we must use a unit quaternion, which means its magnitude is 1:
Quaternions and the Axis-Angle Representation
The real power of quaternions is how elegantly they encode a rotation. A quaternion directly represents a rotation of angle
This problem is really hard using Euler, Rotation-About-An-Axis.
The conversion is given by:
This axis-angle formulation is what allows quaternions to represent any 3D orientation smoothly and without singularities.
Properties
- Addition and subtraction: Quaternions can be added and subtracted component-wise, similar to vectors.
- Multiplication: Quaternion multiplication is not commutative (i.e.,
). The multiplication of two quaternions combines their rotations.
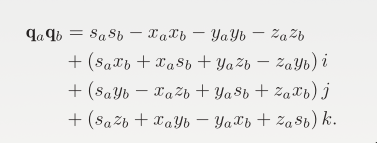
- Conjugate: The conjugate of a quaternion
is given by . This operation is useful for reversing rotations.
- Norm: The norm (or magnitude) of a quaternion is given by
. For unit quaternions, this norm is 1. - Inverse: The inverse of a unit quaternion
is simply its conjugate, i.e., . Otherwise it's given by:
- Rotation of a vector: To rotate a vector
in 3D space using a quaternion , we first represent the vector as a pure quaternion . The rotated vector is obtained by:

Conversion Between Quaternions and Other Representations
From Quaternion to Rotation Matrix
A unit quaternion
Advantages of Quaternions
- No Gimbal Lock: This is the most significant advantage. Quaternions provide a continuous and singularity-free representation of all 3D orientations.
- Computationally EfficientComposing two rotations (multiplying two quaternions) is computationally faster than multiplying two 3x3 matrices. They also use less memory (4 vs. 9).
- Smooth Interpolation (SLERP):Quaternions allow for a constant-speed interpolation between two orientations called Spherical Linear Interpolation (SLERP). This is crucial for generating smooth trajectories for robot arms or cameras. Euler angle interpolation, in contrast, is jerky and the speed of rotation is not constant.
Disadvantages of Quaternions
- Not Intuitive: Their biggest drawback is that these deepshits are very difficult for humans to visualize. It's hard to look at the four numbers of a quaternion and immediately understand the orientation it represents, unlike the simple roll, pitch, yaw of Euler angles. But who cares when the machine can understand it better? insert AI joke