What? Why?
Epipolar geometry describes the geometric relations in image pairs. It enables faster search for prediction of corresponding points between images by reducing the search space from 2D to 1D.
Not only this but this 1D is special because in your image you might have multiple objects which are similar in nature and you can get a wrong correspondence by traversing the entire image. But with epipolar geometry you are reduced to searching in this one line which is somewhat geometrically consistent and your chances of getting wrong correspondences are reduced.
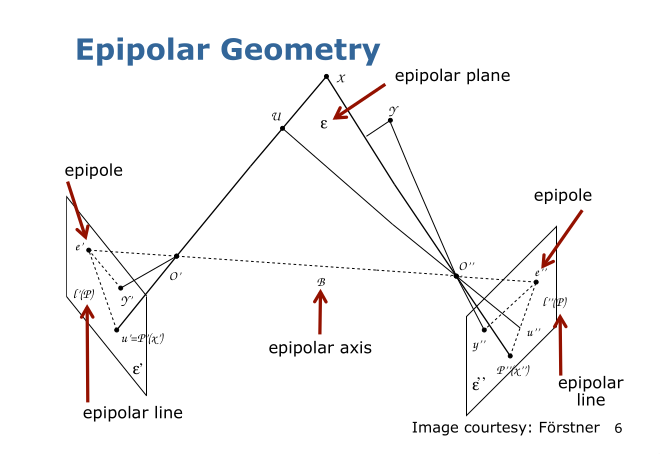
Terms:
- Epipolar Axis: The line connecting the two projection centers. (
). - Epipolar Plane: The plane formed by a 3D point and the two projection centers. (
) - Epipoles: The projections of each camera's center onto the other's image plane. (
, ) - Epipolar Lines: The intersection of the epipolar plane with each image plane. (
, )
In the Epipollar Plane..
Using a distortion-free lens,
- the projection centers
and - the point
- the projections
and are known. ( image points ) - the epipolar lines
and - the epipoles
and
all lie in the same epipolar plane.
Epipolar Constraint
If the point lies on the image plane, then its corresponding point must lie on the corresponding epipolar line. This is called the epipolar constraint.
Also for any point x lying on a line l, the relation
Therefore,
and exploiting the coplanarity of the points X',X''.
As
The epipoles satisfy the relations:
Epipoles are the null space of the fundamental matrix.
They correspond to an eigenvalue of 0.
Fundamental Matrix
- The fundamental matrix F is a 3x3 rank 2 matrix that relates corresponding points in stereo images. It encapsulates the epipolar geometry between two views.
- F has 7 DOF (one DOF is lost due to the scale ambiguities of the homogeneous coordinate space and the other is lost due to the rank-deficiency constraints). Essential matrix E has 5 DOF.
- Defined upto any arbitrary scale factor.
- The fundamental matrix can be computed using a set of corresponding points between the two images. At least 8 point correspondences are needed to compute F using the 8-point algorithm.
Where
So if we have n corresponding points, we can set up a system of linear equations to solve for the entries of F.
Where A is the matrix of coefficients from the corresponding points, and f is the vector of entries of F. A is of size n x 9. and it's rank is 8.
Use normalization to improve numerical stability. Solve using SVD. Enforce rank-2 constraint by setting the smallest singular value to zero.
if you want rank 3:
Enforce rank 2, or
Where
Computation of F is done over n correspondence, to improve we can run RANSAC to filter out outliers.
Note: F is computed on the transformed image if
other methods for finding F: Normalized 8-point algorithm, 7-point algorithm, 5-point algorithm.
Essential Matrix
The essential matrix E is a 3x3 rank 2 matrix that relates corresponding points in calibrated stereo images.
- E has 5 DOF (3 for rotation, 2 for translation direction). It is defined upto scale.
- E can be computed from the fundamental matrix F if the intrinsic camera parameters K and K' are known:
-
so $$F = K''^{-T} E K'^{-1}$$
- The essential matrix can also be computed directly from corresponding points in calibrated images using the 8-point algorithm, similar to the fundamental matrix. As it holds the following epipolar constraint:
Where
Chirality and Pose Recovery
We get 4 motion pairs from
So 4 possible pairs would be:
( The following is not true, pls read page 277/673 in Multiple View Geometry for correct understanding ) ( It's Section 9.6.2 in the book )
Where
To determine the correct pair, we can use the chirality condition which states that the reconstructed 3D points must lie in front of both cameras. We can triangulate a point using each of the four motion pairs and check the depth values. The correct motion pair will yield positive depth values for the majority of points.