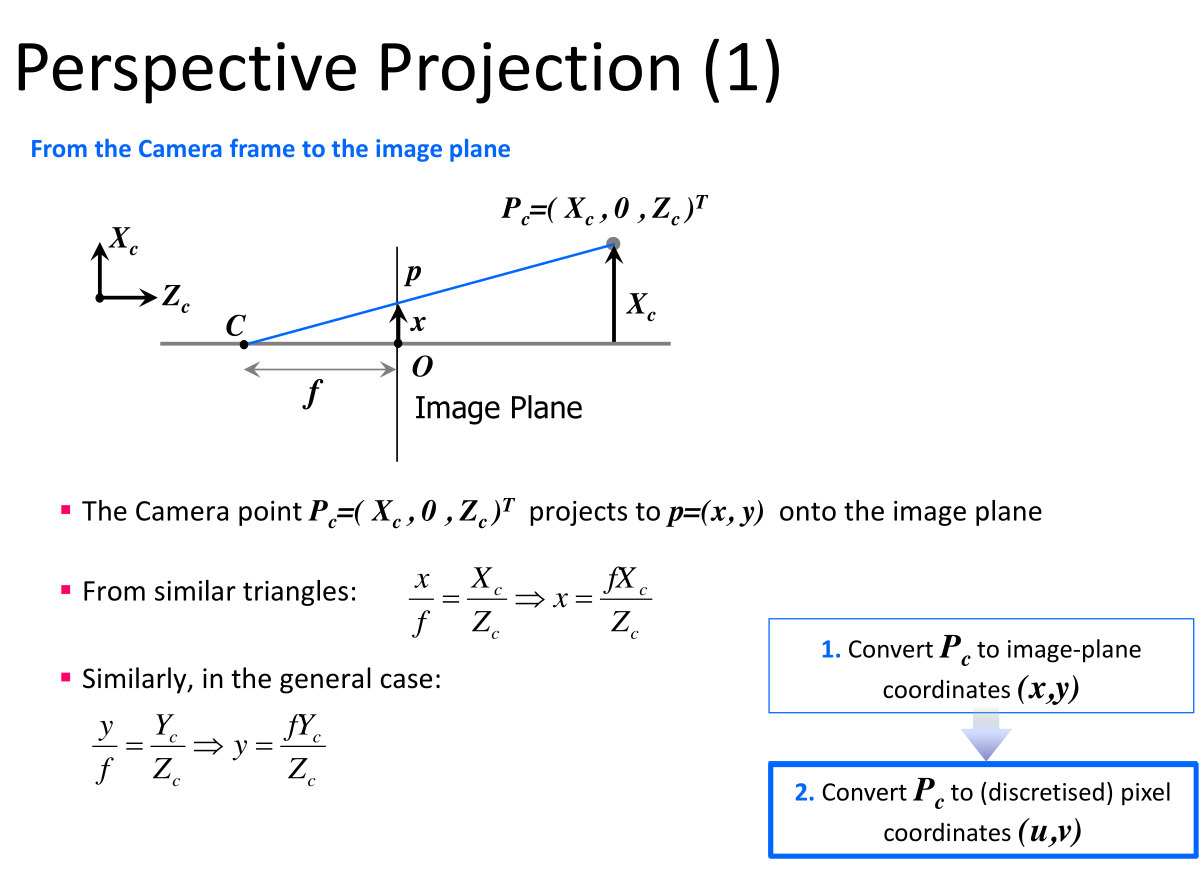
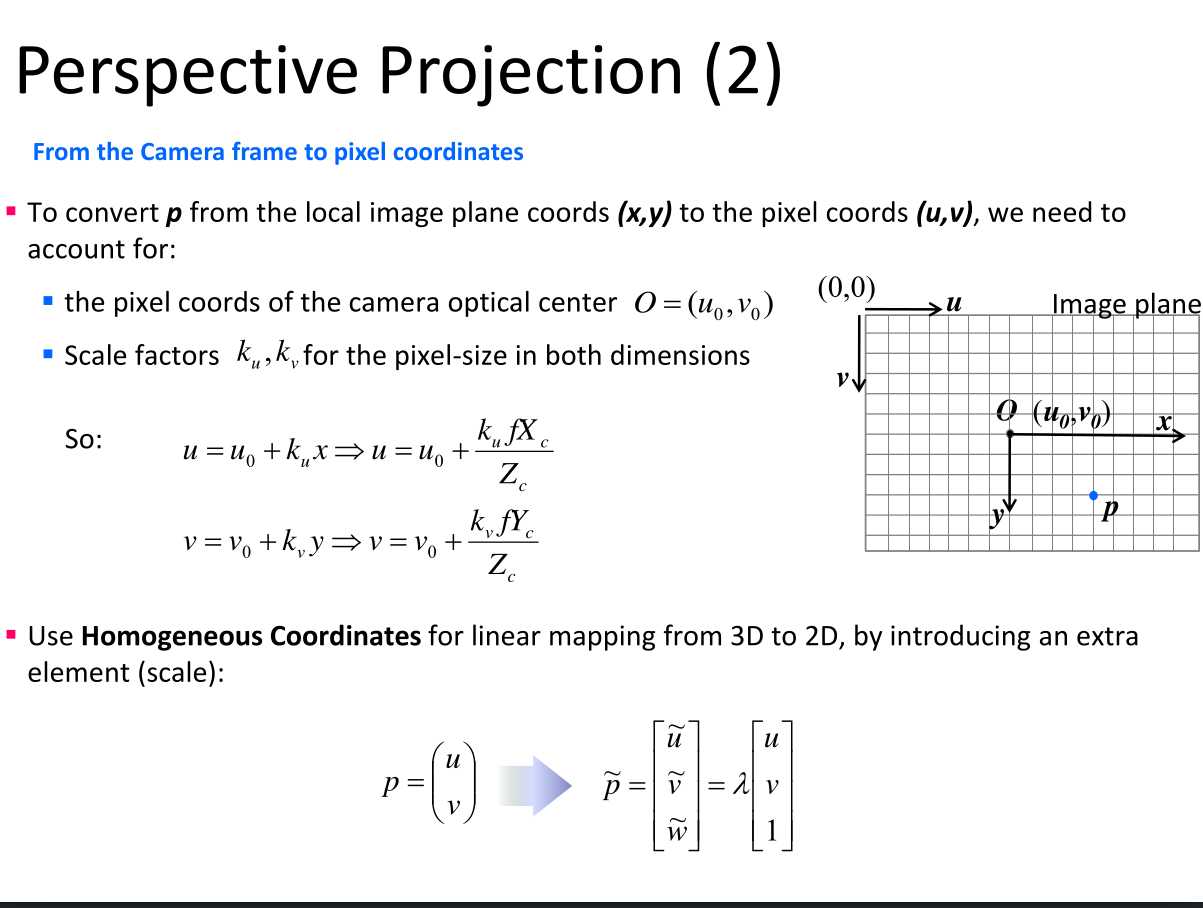
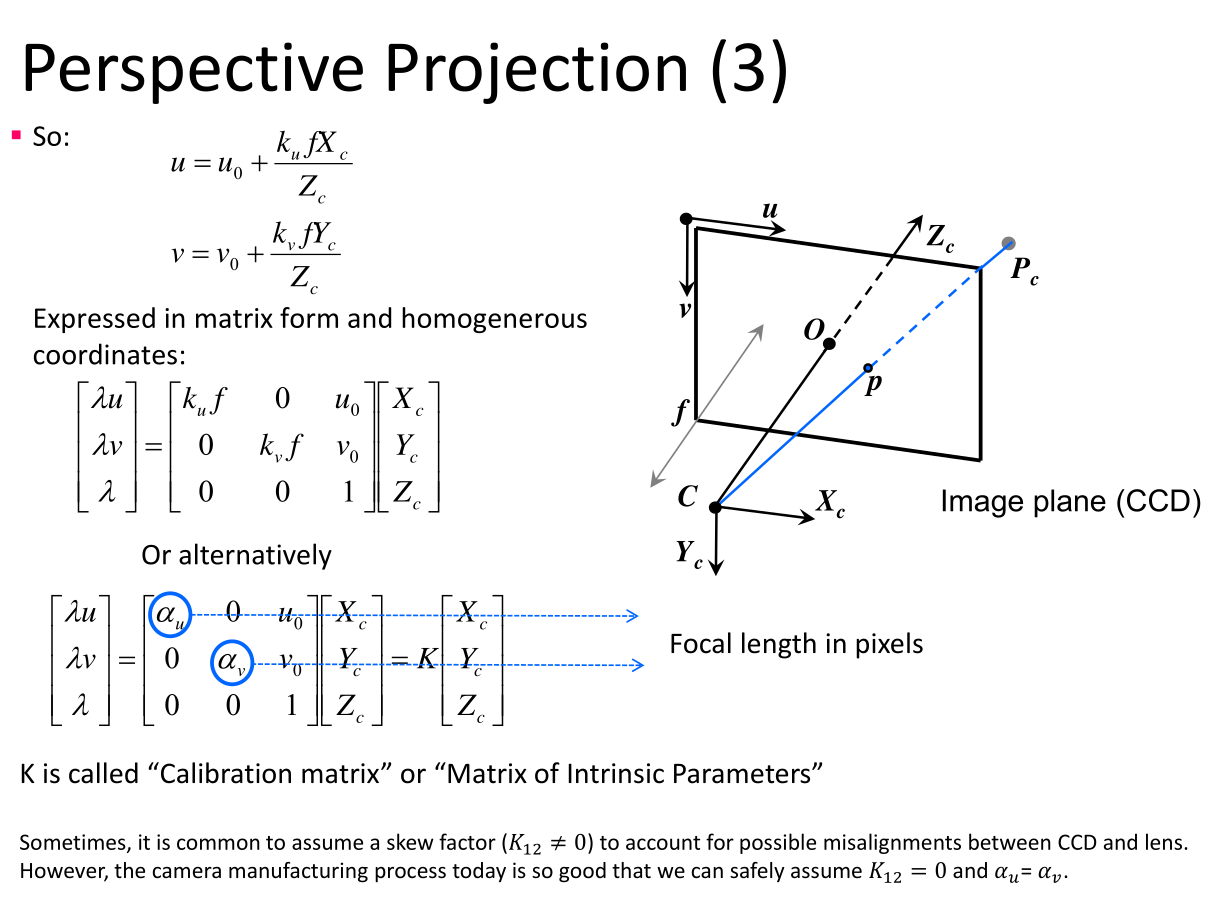
Perspective Projection
Q) Determine K for a digital camera with Image Size 640 x 480 and horizontal field of view equal to
- So because principal point is in center
and and . - And because of:
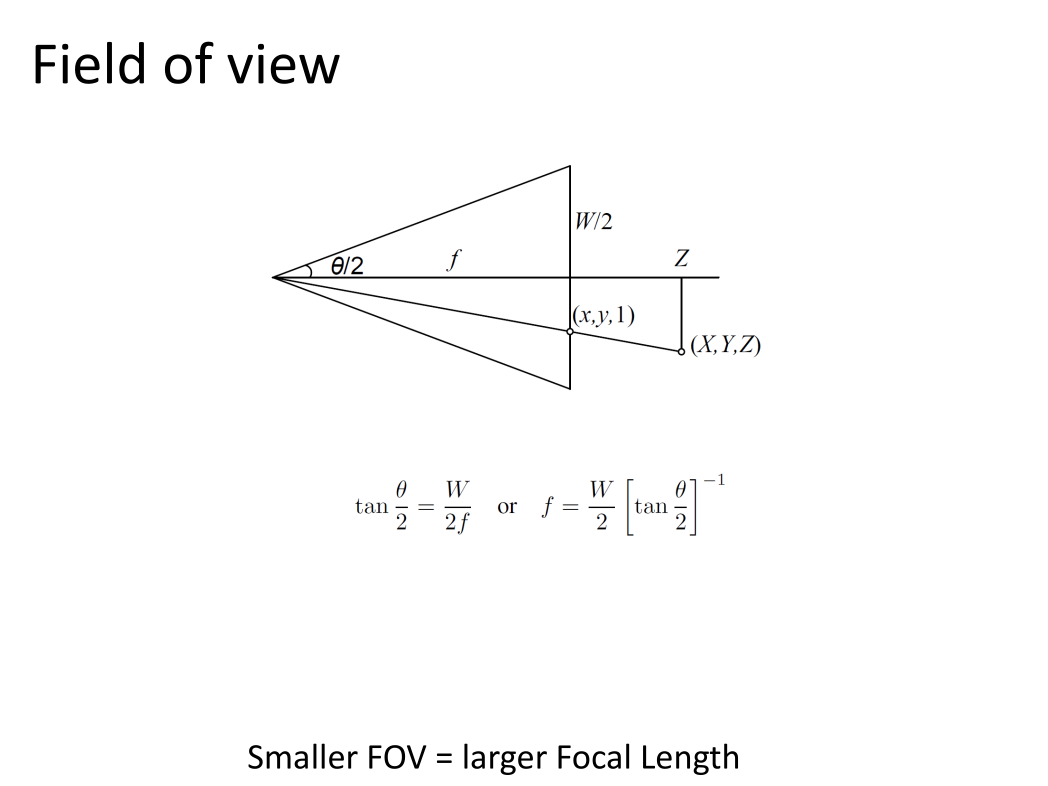
- We also have that
because of squared pixels. , so - Vertical fov can be calculated as:
The Proof: Why Parallel Lines Meet
To Prove: Show that two parallel lines in the 3D world project to lines in the image that intersect at a single specific pixel (the Vanishing Point
- Define Parallel Lines in 3D
Two lines are parallel if they have the same direction vector but different starting points.
Let's define the direction vector as.
-
Line A: Starts at point
.
Equation: -
Line B: Starts at a different point
.
Equation:
Here,
- Apply the Camera Projection
Recall the basic pinhole projection equations (assuming standard camera frame where focal length is
Let's substitute our line equations into this projection.
For Line A:
For Line B:
- Take the Limit (The "Vanishing" part)
For
For
same for Line B:
Both lines converge to the exact same pixel coordinate:
This point
Therefore, all lines with direction
THE Projection Equation
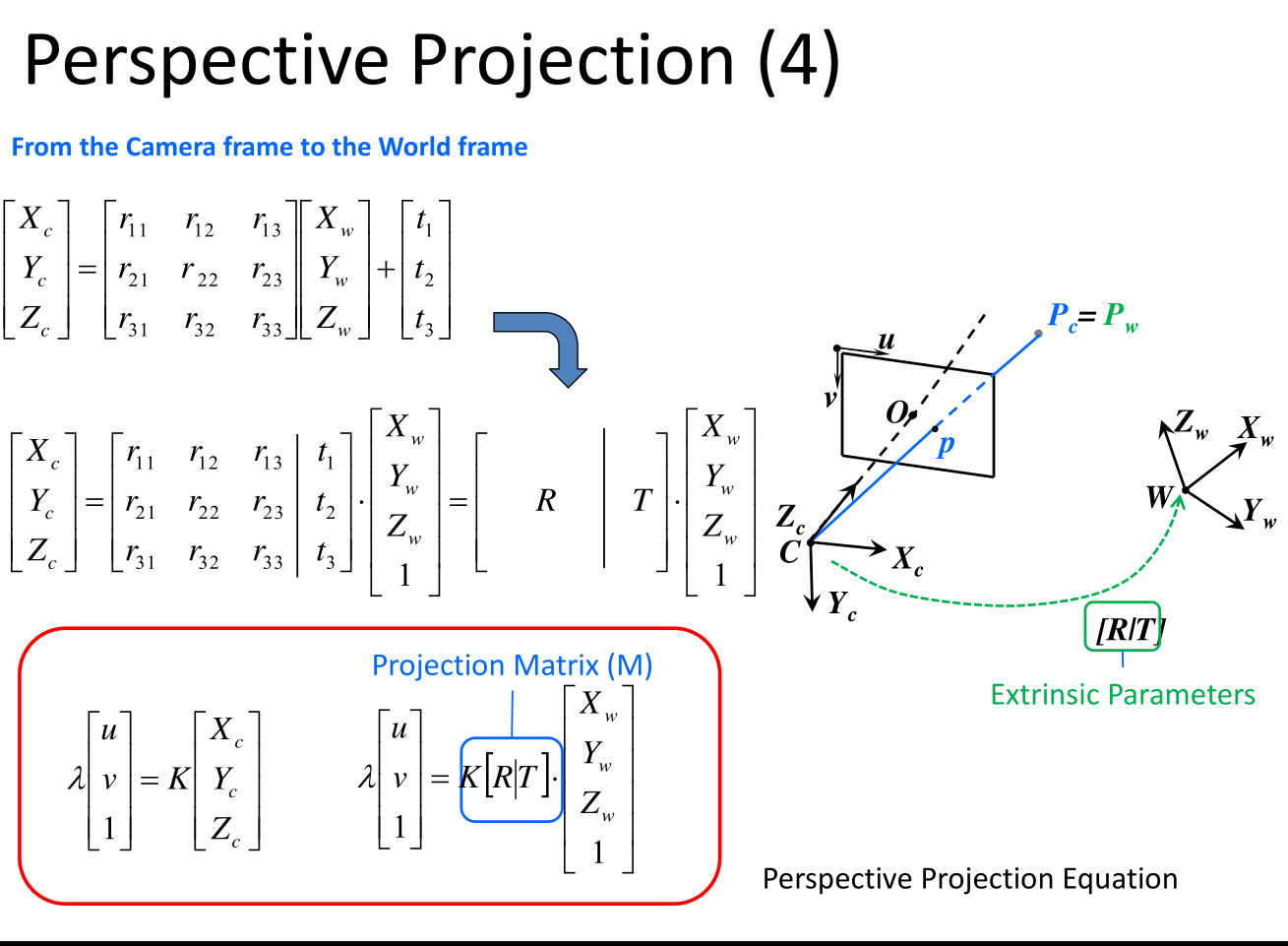
or in Camera Coordinates:
Henceforth
Radial Distortion
For most lens it would just be quadratic but higher order terms can be introduced:
Camera Caliberation
Camera Resection
Pose Problem -- Camera Resection